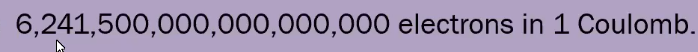- Flow of charge
- Ehen ends of conductor are different charges, electrons flow
- the flow persists as long as there is a difference
- Electric Current
- Flow of electrons == electric current
- 1amp == 1 colomb per second
- amp == amperes
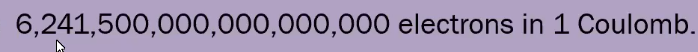
- $$ 6.2 * 10^{18} $$
- Difference between charges is potential difference, EMF, electromotive force
- Conventional Current
- assume postice flows to negative
- Electrical Resistance
- quality to reduce current of current
- depends on
- temperature
- length
- cross section
- area
- Ohms Law
- the current proportional to current
- $$voltage = current * resistance$$
- Electric power
- Watts
- $$power = current * voltage$$
- Electric Circuit
- Series
- Run through multiple points
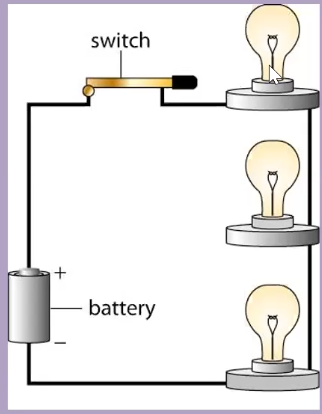
- Less energy as it goes on, and drops proportional to resistance
- Parallel
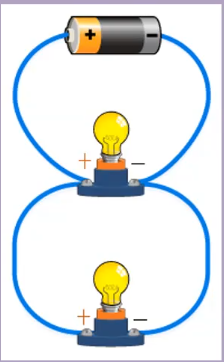
- more paths == less resistance
- $$\frac{1}{resistance} = \frac{1}{resistance_1} + \frac{1}{resistance_2} + ...$$
- Same voltage, different current
- current divided among parallel branches
- current can get very high